The different maritime zones can be defined by first determining the baseline. The baseline is the low-water line or low-tide elevation along the coast which includes its islands at the highest tide level. Seaward will be the different maritime zones, while landward will be the internal waters.
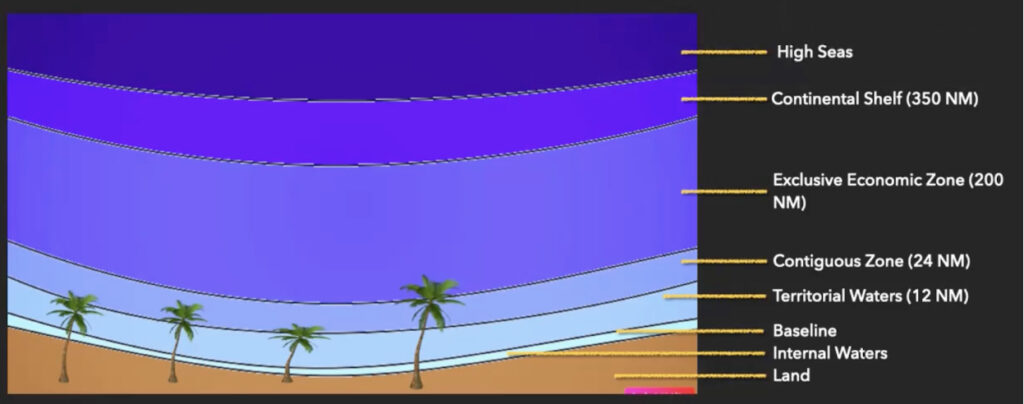
The different maritime zones are:
Territorial Waters
This zone extends from the baseline up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) seaward from the coast of the coastal state. Here, the territory of the coastal state is absolute. This means, it has full sovereignty here including the right to regulate fishing, navigation, and control the use of resources within the zone.
Contiguous Zone
This zone extends up to 24 nautical miles (44.4 km) from the baseline of a coastal state and is adjacent to the territorial waters. Here, the coastal state has limited control to prevent infringement of its laws in the areas of customs, immigration, and sanitation.
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
This zone extends up to 200 nautical miles (370.4 km) from the baseline of a coastal state. The coastal state has sovereign rights over the natural resources in the EEZ, including fish stocks, oil and gas reserves, and minerals. However, other states have the right to some activities over the EEZ such as overflight and navigation, subject to compliance with the laws of the coastal state such as environmental protection.
Continental Shelf
a geological feature that extends from a coastal state’s land territory into the adjacent seabed and subsoil, where the depth of the water is usually shallow. It is subject to the sovereignty of coastal states. The rights to the continental shelf extend up to 200 nautical miles (370 kilometers) from the baseline of a coastal state, or beyond that limit if the shelf extends beyond this distance.
The “High Seas”
It is the “heritage of humankind.” These are essentially the areas of the ocean that do not fall under the jurisdiction of any individual state. It is open to all states and subject to freedom of navigation, which means that ships of all nations have the right to sail on the high seas without interference from other states.